How Do All-Electric Cars Work?
Posted on June 25, 2024 by bike_ev_admin
Electric Car
All-electric vehicles (EVs), also known as battery electric vehicles (BEVs), represent a significant shift from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Instead of burning fuel, they rely on electric motors powered by electricity stored in a large battery pack. Here’s an in-depth look at how they work and their key components:
How All-Electric Cars Work
- Electric Motor Instead of ICE:
- BEVs use an electric traction motor to drive the wheels, eliminating the need for an internal combustion engine.
- Traction Battery Pack:
- A large traction battery pack stores the electrical energy needed to power the electric motor. This battery must be charged by plugging the vehicle into a power source, such as a wall outlet or charging station.
- Zero Emissions:
- Since all-electric cars run on electricity, they produce no exhaust emissions, making them environmentally friendly. They also lack typical fuel system components like fuel pumps, fuel lines, and fuel tanks.
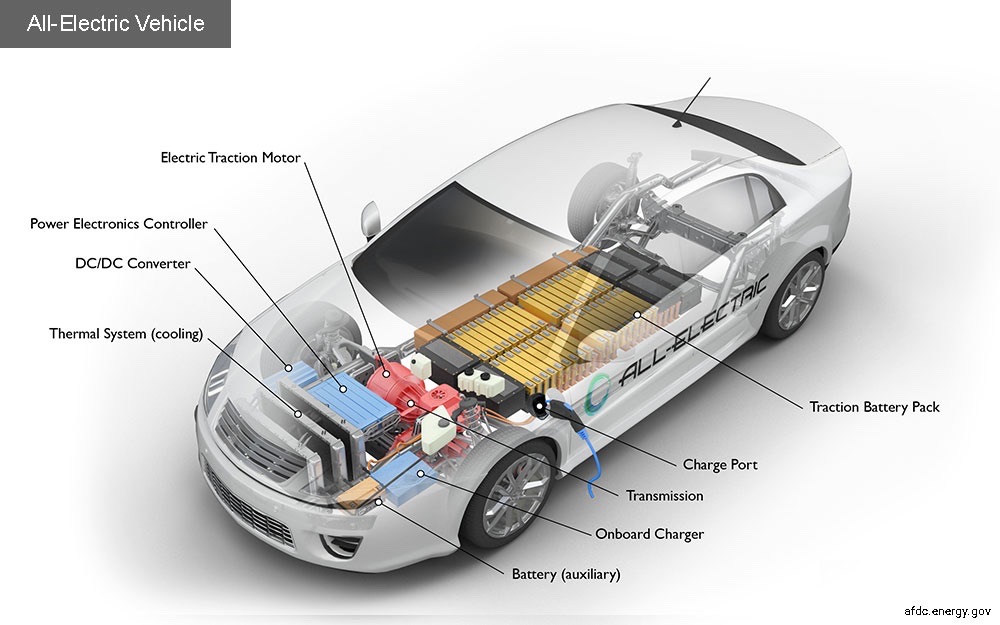
Key Components of an All-Electric Car
- Battery (Auxiliary)
- Purpose: Powers vehicle accessories like lights, infotainment systems, and other electronic devices.
- Function: Provides electricity separate from the main traction battery.
- Charge Port
- Purpose: Connect the vehicle to an external power supply to charge the traction battery.
- Function: Allows the vehicle to be plugged into a charger to replenish the battery pack.
- DC/DC Converter
- Purpose: Converts high-voltage DC power from the traction battery to low-voltage DC power.
- Function: Powers vehicle accessories and recharges the auxiliary battery.
- Electric Traction Motor
- Purpose: Drives the vehicle’s wheels.
- Function: Converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle. Some models use motor generators that also perform regenerative braking.
- Onboard Charger
- Purpose: Converts AC electricity from the charge port to DC power for the traction battery.
- Function: Manages the conversion process, communicates with the charging station, and monitors battery characteristics such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge.
- Power Electronics Controller
- Purpose: Manages the flow of electrical energy to the motor.
- Function: Controls the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it generates by regulating electrical energy flow from the battery.
- Thermal System (Cooling)
- Purpose: Maintains optimal operating temperatures.
- Function: Keeps the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components within their proper temperature ranges to ensure efficient operation and prevent overheating.
- Traction Battery Pack
- Purpose: Stores electrical energy for the electric traction motor.
- Function: Provides the necessary power to the motor for driving the vehicle.
- Transmission (Electric)
- Purpose: Transfers mechanical power from the electric motor to the wheels.
- Function: Facilitates the delivery of power to the wheels, typically with fewer gears than traditional transmissions due to the high torque of electric motors.
Advantages of All-Electric Cars
- Environmental Impact: Zero tailpipe emissions reduce pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Efficiency: Electric motors are generally more efficient than internal combustion engines.
- Maintenance: Fewer moving parts result in lower maintenance requirements.
- Performance: Instant torque from electric motors provides quick acceleration and responsive driving.
Conclusion
All-electric cars represent a major advancement in automotive technology, emphasizing sustainability, efficiency, and performance. By understanding the key components and their functions, one can appreciate the innovation and engineering that make these vehicles a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars.

Leave a Reply